UNIT 4 : PLANTS
CHARACTERISTICS OF PLANTS
The roots take in water from the soil. The stem holds the plant up. The leaves take in air and sunlight. The flowers are colourful and produce seeds for the reproduction of the plant. Today we drew the plant and its different parts.
Las raíces absorben el agua de la tierra. El tallo mantiene erguida a la planta. Las hojas reciben el aire y la luz del sol. Las flores son coloridas y producen semillas para la reprodución de la planta. Hoy hemos dibujado una planta y sus partes.
PLANT EXPERIMENT
2ºB group sowed different plant seeds (oregano and peppermint) in two plant pots. We water the seeds every day. We want to see what it grows! We can't wait to see it!
El grupo de 2ºB plantó diferentes semillas (orégano y hierbabuena) en dos macetas. Regamos las semillas todos los días. Queremos descubrir que crecerá. !No podemos esperar para verlo!
PLANTS ARE LIVING THINGS
We started our last unit in Natural Science, unit 4 "Plants" and we went to talk about them to the playground and we visited part of our garden . Plants are living things. They are born, they grow , the reproduce and they die.
Comenzamos la unidad 4 "Las Plantas" , nuestra última unidad de ciencias naturales, bajamos al patio para hablar de ellas y visitamos nuestro huerto. Las plantas son seres vivos. Nacen. crecen, se reproducen y mueren.
We started by explaining what plants need to live and then we went to the garden to see the different plants there are at school. To watch photos of our visit to the garden, click on the picture.
Empezamos explicando lo que las plantas necesitan para vivir y después fuimos al huertto para ver las diferentes plantas que hay en el colegio. Para ver fotos de nuestra visita al huerto pincha en el dibujo.
UNIT 3: ANIMALS
HERBIVOROUS ANIMALS
VERTEBRATE AND INVERTEBRATE ANIMALS
Animals are classified into vertebrates and invertebrates. Vertebrates have a backbone inside their bodies. Invertebrates don´t have a backbone inside their bodies. Humans are vertebrates.
Los animales se clasifican en vertebrados e invertebrados. Los animales vertebrados tienen una columna vertebral en su cuerpo. Los animales invertebrados no tienen columna vertebral. Los humanos somos vertebrados.
Vertebrates have a backbone. Mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish are vertebrates. Insects and spiders are invertebrates. Many invertebrates are very small.
Los animales vertebrados tienen una columna vertebral. Los mamíferos, los pájaros, los anfibios y los peces son animales vertebrados. Los insectos y las arañas son invertebrados. Muchos invertebrados son muy pequeños.
National geographic kids : vertebrate and invertebrate animals
https://kids.nationalgeographic.com/animals
British council :vocabulary about animals
https://kids.nationalgeographic.com/animals
DK Endangered Species
https://www.dkfindout.com/us/more-find-out/special-events/endangered-animals/
LIVING THINGS AND NON LIVING THINGS
Living things and non living things are all around us. Animals and plants are living things. Animals belong to the animal Kingdom. Plants belong to the Plant kingdom.
Los seres vivos y los seres inertes están a nuestro alrededor. Los animales y las plantas son seres vivos. Los animales pertenecen al reino animal. Las plantas pertenecen al renio vegetal.
UNIT 6 : MACHINES AND TOOLS
THURSDAY 28th APRIL 2021 (2ºA)
After those pages we saw "Coco's story" and we did all the activities in pages 104 and 105. (Después de esas páginas vimos "La historia de Coco" e hicimos las actividades de las páginas 104 y 105.)
TO KNOW MORE ABOUT MACHINES
More activities
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1yDB_VUYESfXLZ7dpoUhEIs6Ba3on_qHb/view?usp=sharing
WORKING ABOUUT SIMPLE MACHINES
SIMPLE MACHINES
We use machines every day at home and in the classroom. Machines make work easier and they can help us move objects. Machines can help us lift, push and pull things. Simple machines have one or two parts. A wheel and axle, a lever, a pulley, a wedge, a screw and an inclined plane are all simple machines.
Usamos las máquinas todos los días en casa y en la clase. Las máquinas nos hacen el trabajo más fácil y nos pueden ayudar a mover objetos. Las máquinas pueden ayudarnos a levantar, empujar o tirar de cosas. Las máquinas simples están compuesta de una o dos partes. Una rueda y su eje, una palanca, una polea, un calzo, un tornillo y un plano inclinado (rampa) son máquinas simples.
The Wheels
UNIT 5 : MATTER AND MATERIALS
TUESDAY 6TH APRIL 2021
Today we revised unit 5 "Matter and materials" with 2ºC. Here you have the worksheets that we did in class and the photos of the whiteboard if you were not in the class.
Hoy repasamos la unidad 5 "La materia y los materiales" con 2ºC. Aquí tenéis las fichas que hicimos en clase si os perdísteis esta clase por estar enfermos.
THE THREE STATES OF MATTER
MIXTURES
A mixture is made when two or more subtances are combined. Mixtures can be homogeneous or heterogeneous. In a homogeneous mixture , ingredients mix together easily. In a heterogeneous mixture, ingredients don't mix together easily.
Una mezcla se produce cuando dos o más sustancias se combinan. Las mezclas pueden ser homogéneas o heterogéneas. En una mezcla homogénea, los ingredientes se mezclan muy facilmente. En una mezcla heterogénea, los ingredientes no se mezclan fácilmente.
Watch these videos to understand what mixtures are. (Ve los vídeos para entender que son las mezclas)
PROPERTIES OF THE DIFFERENT MATERIALS
Materials have different properties. They can be hard or soft, transparent or opaque, rigid or flexible. Glass is transparent. Cotton is soft. Wood is rigid. Some metals are attracted to magnets.
Los materiales tienen diferentes propiedades. Pueden ser duros o blandos, transparentes u opacos, rígidos o flexibles. El cristal es transparente. La madera es rígida. Algunos metales son atraídos por los imanes.
There are many types of materials, but some of them are waterproof. Waterproof materials are water-resistant. They don't let any water through. Objects made from rubber or plastic are waterproof because they don't let water through.
Hay muchos tipos de materiales, pero algunos de ellos son resistentes al agua. Los materiales waterproof son resistentes al agua. Los objetos hechos de goma o plástico son resistentes al agua porque no dejan que el agua penetre en ellos.
MAGNETISM
Magnets are magnificent objects that create an area of magnetic force around them which is invisible to the human eye.This area is known as magnetic field. If a magnetic object is inside that area it gets attracted toward the magnet.
Los imanes son objetos geniales que crean un áre de fuerza magnética alrededor de ellos lo cuál es visible al ojo humano. Este área es conocido como campo magnético. Si un objeto magnético está dentro de esta área es atraído hacia el imán.
SINK OR FLOAT (Thursday 25th February 2021)
Hypothesis song
Bouyancy is the ability to float in liquid. A beach ball is very buoyant, where a marble is not buoyant at all. It's because the ball of air is less dense than the water.
La flotabilidad es la habilidad de flotar en líquido. Una pelota de playa flota muy bien, mientras que una canica no flota. Es porque la pelota inflable es menos densa que el agua.
Cookie monster 's experiment
Sink or float explanation
UNIT 2 : INTERACTION
MONDAY 18th JANUARY
Activities for today
Do pages 24, 25, 26 and 27 of your Natural Science book (Some pages were done during the lasta days of December)
Haz las páginas 24, 25, 26 y 27 de tu libro de ciencias naturales (Algunas páginas se hicieron en algunos cursos durante los últimos días de diciembre)
You can also watch a video to revise these contents (Puedes ver un vídeo además para repasar los contenidos)
Audios
Audio page 24 theory and exercise 1
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ArMp47HhfcW20WXDMTce-oVEvXkV3Ug0/view?usp=sharing
Ejercicio
https://drive.google.com/file/d/13YZ59bgdyhbR5MNS37s1ec3D9j_eRESi/view?usp=sharing
Audio page 24 exercise 4
Chant
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1yulBkRX3fqvcTaX6juihCamtrkkJNtPX/view?usp=sharing
Audio page 25
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1YSrD59zatFapMTc3t_uGfQkcYlxARhJ2/view?usp=sharing
Audio page 26 exercise 3
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1SkEi1FFDovETj1BUHd9iktAwc1PCVL8y/view?usp=sharing
Ejercicio
https://drive.google.com/file/d/16xlfmbho68vb9Wr-w5A7H-jfCKuaSOtJ/view?usp=sharing
JUEVES 14 DE ENERO 2021
SENSES SONG - Canción de los sentidos(14-1-2021)
MUSIC - click on the link (Música - Pincha en el enlace)
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1mN5VkjLUbbCjENOVmXIc30A4VfK0nj5W/view?usp=sharing
LYRICS
"I use my eyes to see
I use my eyes to see
to see paintings and landscapes
I use my eyes to see.
I use my ears to hear
I use my ears to hear
To hear traffic and people
I use my ears to hear.
I use my nose to smell
I use my nose to smell
to smell flowers and perfume
I use my nose to smell.
I use my tongue to taste
I use my tongue to taste
to taste food and drink
I use my tongue to taste.
I use my hands to touch
I use my hands to touch
to touch hard things and soft things
I- use my hands to touch"
HEALTHY HABITS
We only have one body. We need to take care of our body to have healthy bones and muscles and a healthy brain.
Sólo tenemos un cuerpo. Necesitamos cuidarlo para tener unos músculos y huesos saludables y también un cerebro sano.
EAT HEALTHY FOOD
Food is like fuel for your body. It is what gets you up and keeps you moving. Your body turns the food you eat into chemicals called nutrients, which it needs for everything. Food keeps your bones healthy and strong. It maintains and repàirs your tissues. It gives you energy. It mantains and repairs your tissues. It powers your body and it powers your brain.
La gasolina es el combustible de tu cuerpo. Es lo que te hace levantarte y mantenerte en movimiento. tu cuerpo convierte la comida en sustancias químicas llamadas nutrientes, que se necesitan para todo. La comida mantiene tus huesos sanos y fuertes. Mantiene y repara tus tejidos. Te da energía. Fortalece tu cuerpo y tu cerebro.
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM (EL SISTEMA NERVIOSO)
We have a brain inside our heads. Different parts of your brain control different activities, but how does your brain tell all the parts of your body what to do? And, in return, how do your eyes,ears, and nose tell your brain what they see, hear, and smell? The answer is your nerves.
Tenemos un cerebro en nuestra cabeza. Hay diferentes partes del cerebro que controlan actividades diferentes pero ¿cómo te dice tu cerebro a todas las partes de tu cuerpo lo que tienen que hacer? Y, al revés, ¿cómo le dicen tus ojos, oídos y nariz lo que ven, oyen o huelen? La respuesta es por medio de tus nervios.
Los nervios - estructuras delgadas similares a hilos - llevan mensajes de tu cerebro a el resto de tu cuerpo en ambas direcciones. Los nervios recorren tu columna vertebral y se ramifican hasta tus dedos de las manos y de los pies. El sistema nervioso controla tu cuerpo, les dice a tus músculos que se muevan y te deja que experimentes el mundo que te rodea. Los nervios son parte de tu sistema nervioso, que incluye también a tu cerebro y a tu médula espinal.
Your nerves are made of cells called neurons. Neurons send and receive messages between your brain and the other parts of your body by sending out alternating electrical and chemical signals. Messages flash from neuron to neuron along your nerves and inside your brain. Signals from your eyes might tell the brain, "There is my bus" The brain then sends signals that zoom from cell to cell making sense of the message. Then the brain sends signals back down to the nerves connected to your leg muscles to say, "Run to the bus stop!"
Tus nervios están hechos de unas células llamadas neuronas. Las neuronas envían y reciben mensajes entre tu cerebro y otras partes de tu cuerpo mandando y alternando señales eléctricas y químicas. Los mensajes se proyectan de neurona a neurona por los nervios y dentro de tu cerebro. Las señales de tus ojos pueden decir al cerebro "Aquí está mi bus" El cerebro entonces envía señales que pasan de célula a célula haciendo que el mensaje tenga sentido. Después el cerebro envía señales a los nervios conectados con los músculos de tus piernas que dicen " ¡Corre a la parada del autobús!
If you want to know more about the brain
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-nH4MRvO-10
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ndDpjT0_IM0
Experiments about the brain
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GUCcsMmZVec
THE SENSE OF TOUCH (EL SENTIDO DEL TACTO)
Touch is one of your "general senses"- a sense you have all over your body. When you feel your cell phone buzz in your pocket, or an itchy mosquito bite your arm, or a cold winter wind on your cheeks, it's because your sense of touch is doing its job.
El tacto es uno de tus "sentidos generales" - un sentido que tienes por todo el cuerpo. cuando sientes tu móvil vibrar en tu bolsillo, o a un molesto mosquito picarte en el brazo, o el viento en invierno en tus mejillas, es porque tu sentido del tacto está haciendo su trabajo.
Your body's biggest organ isn't hidden inside of you. It's your skin - a head to toe wrap that keep your insides in and outside out. Your skin is a flexible, tough barrier that stops germs for entering your body. Your skin also makes oil that contains germs- fighting substances.
El órgano más grande de tu cuerpo no está escondido dentro de ti. Es tu piel - una envoltura desde la cabeza a los pies por dentro y por fuera de tu cuerpo. Es una barrera dura y flexible que evita que los gérmenes penetren en tu cuerpo. Tu piel también contiene aceites que contienen sustancias para lucha r contra los gérmenes.
Through your skin you can feel the heat, the cold, textures, sizes...A través de la piel pueden sentir el calor, el frío, las texturas, los tamaños...
Let's talk about textures. Objects can be sticky, soft, hard, rough, itchy, fluffy, squishy...(Hablemos de las texturas. Los objetos pueden ser pegajosos, blandos, duros, suaves, ásperos, que pican, acolchados o esponjosos...
Let's talk about shape. Objects can be rounded, squared... (Hablemos de la forma. Los objetos pueden ser redondos, cuadrados...)
Let's talk about temperature: Objects can be hot or cold. (Hablemos de temperatura. Los objetos pueden estar fríos o calientes)
If you want to know more about it, click on
More about the sense of touch in general
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mWeTqNdSQlE
What texture is
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CdA4EcEkzzg
Elmo's world : Skin
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V6aX8INal3I
What is Racism? Story
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XopxsSdecbc
THE SENSE OF SMELL (EL SENTIDO DEL OLFATO)
The nose pulls in the air you breathe. It blocks out dusts and germs and it senses 10.000 different smells from the sweet aroma of chocolate chip cookies to the yucky stink of garbage. The smell receptors search the air for smelly chemicals and, if they find any, they send the information to your brain. Your brain sorts out the information and tells you what you smell.
La nariz aspira el aire que respiras. Bloquea el polvo y los gérmenes y distingue 10.000 olores diferentes desde el aroma dulce de las galletas de chocolate hasta el odor apestoso de la basura. Los receptores del sentido del olfato buscan en el aire los elementos olorosos y, si encuentran alguno, envian información al cerebro. Tu cerebro clasifica la información y te dice lo que hueles.
THE SENSE OF TASTE (EL SENTIDO DEL GUSTO)
We taste with our tongue. Your tongue is covered with thousands of sensory organs called taste buds. They are so small you cannot see them, but if you stick your tongue out and look in a mirror, you can see the little pink bumps.
Saboreamos con nuestra lengua. Tu lengua está cubierta de miles de órganos sensoriales llamados papilas gustativas. Son tan pequeñas que no puedes verlas, pero si sacas la lengua y te miras en un espejo ,puedes ver los pequeños bultos rosados.
Your ears are designed to hear even tiny noises and turn them into signals for the brain. Your ears have three parts: outer, middle and inner ear. It starts when the sound enters the outer ear. There, the waves bounce off the tightly stretched skin of the eardrum. Now your middle ear gets into action. The vibrating eardrum makes three teensy bones in your middle ear wobble. The wobbling bones shake the liquid inside a curling tube called the cochlea, located in your inner ear. Tiny hairs lining the cochlea wave back and forth. This tickles nerve cells at their base. Then the nerve cells send a message to the brain to say what they are hearing.
Tus oídos están diseñados para oir incluso ruídos diminutos y convertirlos en señales para el cerebro. Tus oídos tienen tres partes: exterior, medio e interior. Todo comienza cuando el sonido entra por nuestros oído externo. Allí , las ondas rebotan y tensan la piel del tímpano. Ahora es cuando tu oído medio entra en acción. El tímpano vibrante hace moverse a tres pequeños huesos de tu oído. Esos huesecillos agitan un líquido dentro de un tubo en curva llamado cóclea, que está en tu oído interno. Unos diminutos pelos de la cóclea se mueven hacia delnate y hacia atrás. Esto toca las células nerviosas desde su base. Por último las células nerviosas envian un mensaje al cerebro para decir que están oyendo.
Videos about the sense of hearing (Vídeos sobre el sentido del oído)
THE SENSE OF SIGHT (EL SENTIDO DE LA VISTA)
You can see with your eyes. Your eyes are two of the most amazing organs in your body. These small squishy, fluid-filled balls have almost of your body's sensory receptors. They are like two supersmart cameras.
Puedes ver con tus ojos. Tus ojos son dos superórganos de tu cuerpo. Estos pequeños globos llenos de fluido tienen la mayoría de los receptores sensoriales de todo el cuerpo.
THE FIVE SENSES (LOS CINCO SENTIDOS)
The senses - sight, hearing, smell, taste, and touch- are your body's ways of explaining the world to your brain. Your senses help you make sense of the world, and they help keep you safe in it.
Los sentidos - la vista. el oido, el olfato, el gusto y el tacto - son los modos que tiene tu cuerpo de explicarle le mundo a tu cerebro. Tus sentidos te ayudan a comunicarte con el mundo, y además te ayudan a mantenerte a salvo.
BONES, JOINTS AND MUSCLES (part 3)
With its strong bones and flexible joints, your skeleton is built to be on the go. But without muscles, it won't go anywhere.!You need muscle power to make your body walk, run, skip, rub your nose, or even just sit up without toppling over.
Con sus fuertes huesos y articulaciones flexibles, tu esqueleto está hecho para moverse. Pero sin músculos, no iría a ninguna parte. Necesitas el poder de los músculos para que tu cuerpo ande, corra, salte. se frote la nariz o incluso se siente sin caerse.
The muscles that do these jobs are called skeletal muscles. You have about 650 of them, and you can control what they do. Sometimes, it takes a lot of skeletal muscles to make even a simple move. Your tongue alone contains eight muscles!
Los músculos que hacen esas tareas se llaman músculos esqueléticos. Tienes alrededor de 650 músculos esqueléticos y puedes controlar lo que hacen. Algunas veces, se requieren muchos músculos esqueléticos para hacer un movimiento simple. ¡Tu lengua contiene 8 músculos!
You also have muscles that work without you having to do a thing. Most of these muscles are called smooth muscles. Sheets of smooth muscle line your blood vessels, throat, stomach, intestines, lungs and other organs. Thay are hard at work keeping your blood circulating and your food digesting while you're busy doing other things. And there's also that mighty muscle, your heart. It pumps thanks to cardiac muscles, which are found only in the heart.
Tienes además músculos que funcionan sin que tengas que hacer nada. Estos músculos se llaman lisos o involuntarios. Capas de músculos involuntarios se localizan en tus vasos sanguíneos, garganta, estómago, intestinos, pulmones y otros órganos. Trabajan duro para mantener a tu sangre circulando y a tu comida digeriendose mientras tu estás ocupado haciendo otras cosas. Y hay además un músculos muy poderoso, tu corazón. Bombea gracias a sus músculos, que se encuentran solamente en el corazón.
BONES, JOINTS AND MUSCLES (part 2)
Your skeleton is not just stiff and strong. It also bends easily at places where different bones meet. These places are called joints.
Tu esqueleto no es tan rígido y fuerte. También se dobla facilmente por los lugares donde los diferentes huesos se encuentran. A estos lugares los llamamos articulaciones.
Un articulacón está compuesta del final de dos huesos que están atados por unas cuerdas duras llamados ligamentos. Los ligamentos mantienen los huesos en su lugar, como cuerdas fuertes, pero son suficientemente elásticas para permitir el movimiento.
Tu cuerpo tiene más de 400 articulaciones, y muchas de ellas son suficientemente flexibles para moverse de arriba a abajo, hacia los lados o en círculo. Los hombros, los codos, las muñecas, las caderas, las rodillas y los tobillos son articulaciones.
Watch the video and learn more about joints. (Ve el vídeo y aprende más sobre las articulaciones)
BONES, JOINTS AND MUSCLES (part 1)
Your skeleton is a framework made of bones that supports your body and gives it a shape.Without your skeleton you wuold be a jellyfish- like blob. Your skeleton protects your internal organs, too. The ribs, for example, form a sturdy cage around your lungs. Your skull protects your brain.
Tu esqueleto es una estructura formada por huesos que soporta tu cuerpo y le da forma. sin tu esqueleto serías un ser similar a una medusa. Tu esqueleto también protege tus órganos internos. Las costillas, por ejemplo, forman una "jaula" alrededor de los pulmones. Tu cráneo protege tu cerebro.
Watch the videos and see how your skeleton works. (Mira los vídeos y fíjate como funciona tu esqueleto)
Tu esqueleto también hace posible que corras, gatees, saltes, juegues a la pelota...Sus huesos se mueven porque tienen músculos junto a ellos. Cuando un músculo se acciona en un hueso, el hueso se mueve. Pero los huesos son más que estructuras rígidas y fuertes que los músculos utilizan cuando se mueven. Como otras partes del cuerpo, son tejidos vivos que contienen nervios y vasos sanguíneos. Pueden incluso autorepararse , cuando se dañan.
Cartilage is found not only in your nose and your ears but also in many other parts of your body. These body parts are stiff enough to keep their shape, but flexible enough to be bent because they are made of a rubbery material called cartilage.
Most fish have bony skeletons. A shark, however, has a skeleton made of cartilage. The rubbery skeleton makes a shark's body very flexible, which helps it make tight turns as it zooms after pray.
El cartílago se encuentra no sólo en tu nariz y en tus orejas sino en más partes del cuerpo. Estas partes de tu cuerpo son suficientemente rígidas para darles forma. pero suficientemente flexibles para doblarse porque están compuestos de un material gomoso llamado cartílago.
Muchos peces tienen esqueletos de hueso. El tiburón, tiene un esqueleto hecho de cartílago. El esqueleto gomoso del tiburón le permite que su cuerpo sea muy flexible, lo que le ayuda a hacer giros mientras busca a su presa.
Learn some bones of your body playing these games. (Aprende los huesos de tu cuerpo jugando a este juego)
https://www.abcya.com/games/skeletal_system
https://online.seterra.com/en-an/vgp/3800
PARTS OF THE BODY
We remembered the parts of the body today. Watch the video and revise them.
Recordamos las partes del cuerpo hoy. Ve el video y repásalas.
https://www.abcya.com/games/skeletal_system
Today we did exercises 1,2 and 3 of Natural Science book. (Hoy hicimos los ejercicios1,2 y 3 de la página 24 del libro de ciencias naturales)
Today we started a new lesson "Interaction" where we will study bones and muscles and the five senses.
Hoy empezamos la unidad 2 "Intesraction" donde estudiaremos los huesos y los músculos y los cinco sentidos.
Our excretory system helps us eliminate waste products. It has different parts: kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra.
Nuestro sistema excretor nos ayuda a eliminar las sustancias perjudiciales para el cuerpo. Tiene cuatro partes diferentes: los riñones, los uréteres, la vejiga y la uretra.
Our kidneys clean the blood. Urine goes down the ureters into the bladder and then down the urethra.
Nuestros riñones limpian la sangre. La orina baja por los uréteres a la vejiga y después sale por la uretra.
THURSDAY 29 th OCTOBER 2020
Our bodies need oxigen from the air to work . when we breathe, air goes through our nose and into our lungs.
Nuestro cuerpo necesita oxígeno del aire para funcionar. Cuando respiramos , el aire baja por la nariz, la traquea y llega a los pulmones.
There is a video here where you can see the different organs of the digestive system. You can see the process of digesting food.
NATIONAL GEOGRAPHIC FOR KIDS
Watch documentaries and funny videos of your favourite animals, know facts about them and play games.
En esta página web encontrarás documentales de animales, información sobre cada uno de ellos y juegos para disfrutar.
https://kids.nationalgeographic.com/
CARNIVORES, HERBIVORES AND OMNIVORES
Herbivores eat plant. Carnivores eat other animals. Omnivores eat plants and other animals. Giraffes are plants; they are herbivores. Lions eat meat ; they are carnivores. Bears eat meat and plants: they are omnivores.
VERTEBRATE AND INVERTEBRATE ANIMALS
LIVING THINGS AND NON LIVING THINGS
Learn about the differences of living things and non- living things.
Aprende las diferencias entre seres vivos y seres inertes.
UNIT 6: TOOLS AND MACHINES
RECYCLING PROJECT (trabajo voluntario, servirá para subir nota)
Materiales
- Botellas de yogur liquido
- Cartones de cereales
- Rollos de papel higiénico
- Tapones de botellas
- Latas
- Botellas de plástico
- Periódicos y revistas
- Calcetines viejos...
Objetivo
Crear un objeto nuevo a partir de materiales reciclados. Pueden ser máquinas u otros objetos como marionetas, huchas u otras cosas que los alumnos inventen. Aquí os dejo unos modelos de ejemplo.
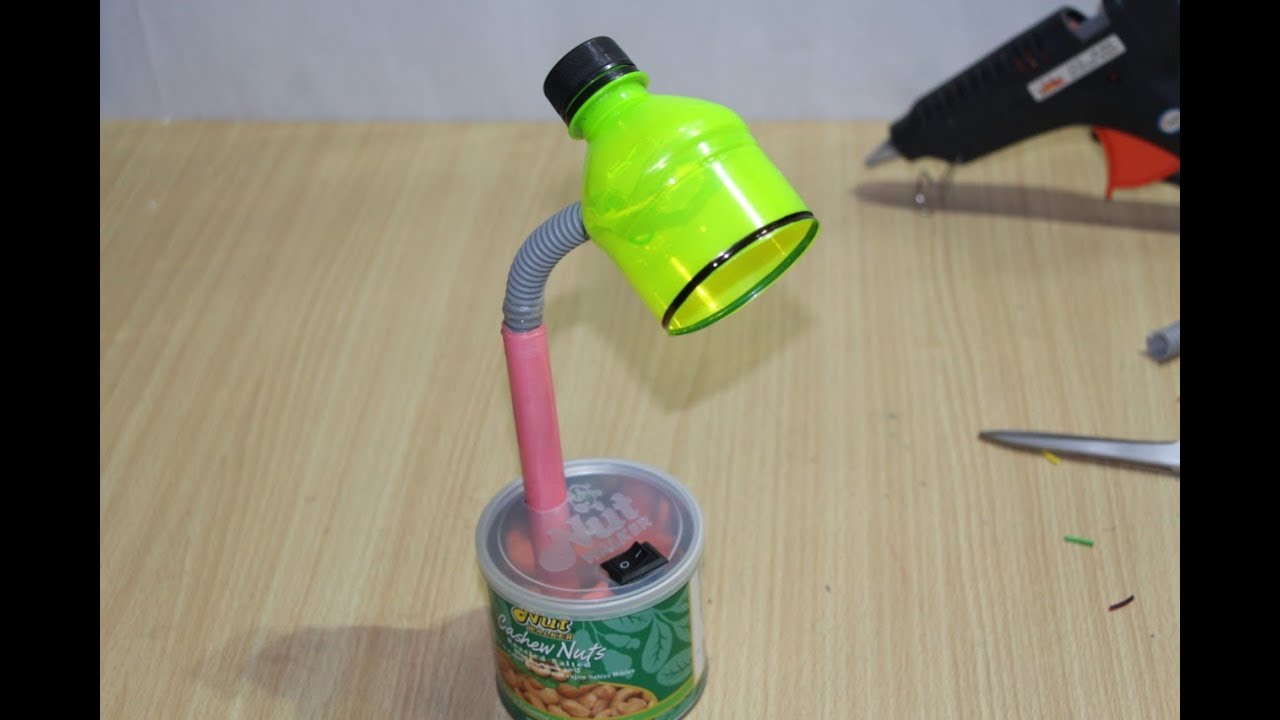
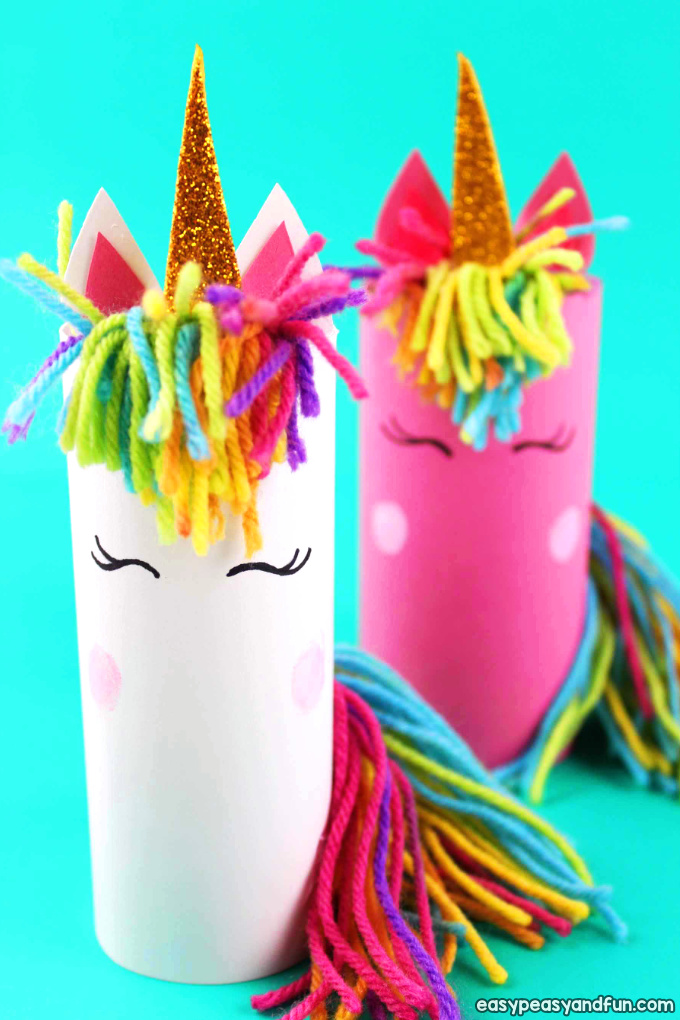



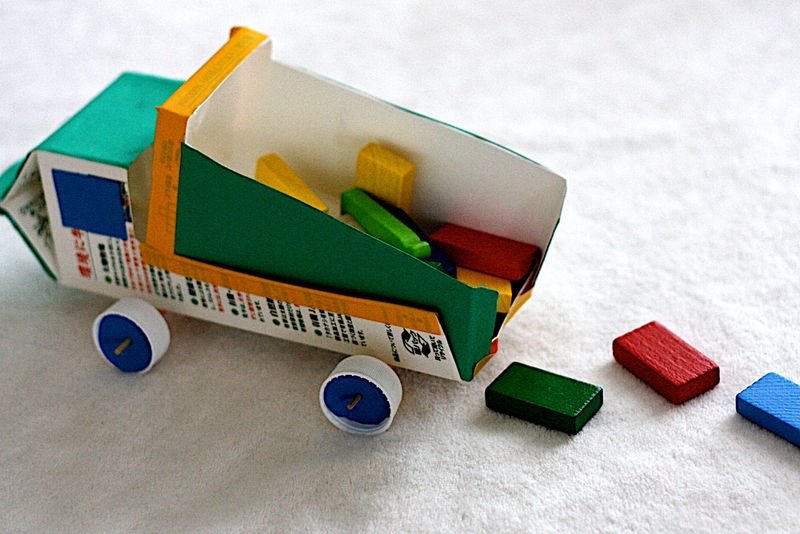



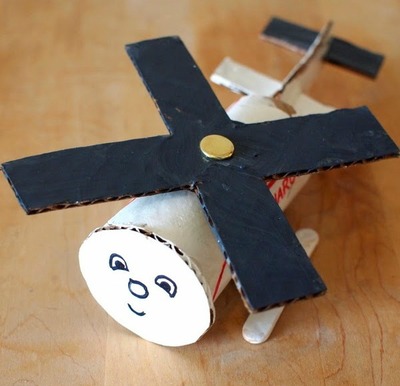









SIMPLE AND COMPLEX MACHINES
WHY DO WE NEED MACHINES?
How will the penguins of this video move the ice rock? Don't you worry! Supergrover will save the day!!
¿Cómpo moverán los pingüinos del video la gran roca de hielo? !No te preocupes! Coco dará con la solución.
UNIT 5 : PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Have a look at the song!!
UNIT 5:MATTER AND MATERIALS
COTTON
WOOD
WOOL
UNIT 2: INTERACTION
OUR SENSES
We have five senses : sight, hearing, smell, taste and touch. We use different parts of our body for each of the five senses.
Tenemos cinco sentidos: vista, oído, olfato, gusto y tacto. Usamos partes diferentes órganos para cada uno de los sentidos.
LEARN ABOUT OUR BONES
SKELETON DANCE
Our locomotor system is made up of bones, muscles and joints. Bones are hard and rigid.
Every single person has a skeleton made up of many bones. These bones give your body structure, let you move in many ways, protect your internal organs, and more.
Nuestro sistema locomotor se compone de huesos, músculos y articulaciones. Los huesos son duros y rígidos.
Cada perdona tiene un esqueleto formado por muchos huesos. Estos huesos dan su estructura al cuerpo, le permiten moverse, protegen los órganos internos y tienen muchas más funciones.
THE PLATYPUS
THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Today we learnt about the circulatory system in science. The blood vessels (veins and arteries ) are in charge of taking the blood to all the body tissues. The heart is the organ responsible for pumping the blood in our body. Watch the video and learn more facts!!
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Watch the video and learn about the digestive system. Aprende sobre el sistema digestivo con este video.
MOVE YOUR BODY
HEAD ,SHOULDER, KNEES AND TOES


































 Today we did exercisesToday we did exercises 1,2 and 3 of Natural Science book. Today we did exercises 1,2 and 3 of Natural Science book. 1,2 and 3 of Natural Science book.
Today we did exercisesToday we did exercises 1,2 and 3 of Natural Science book. Today we did exercises 1,2 and 3 of Natural Science book. 1,2 and 3 of Natural Science book.  Today we did exerciseToday we did exercises 1,2 and 3 of Natural Science book. s 1,2 and 3 of Natural Science book.
Today we did exerciseToday we did exercises 1,2 and 3 of Natural Science book. s 1,2 and 3 of Natural Science book. 















I would like to add yet another link to discover more on our bones:
ResponderEliminarWhy do we have bones? What do they do? What are they called? This animated video shows how bones are important to everyday tasks and movements. The spine, rib cage, tibia, femur and skull are shown within a body shape. Various parts of the body are featured.
https://www.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/ket-earlychild-health1/lets-look-inside-our-body/
BR,
Elena (Irati's mum)